You are encouraged to share this post with your friends, acquaintances, colleagues and family by all channels available to you.
News posts, such as this, published on the SBARC website are reposted via a number of other channels including social media feeds and our Groups.io mailing lists. These external services may alter the formatting or layout of the original News Post. If you want to see this News Post in its original form please visit the SBARC website News page and follow the link or links to the story or stories of your choice.
Amateur Radio on the International Space Station (ARISS) is planning for a special SSTV experiment. ARISS is the group that puts together special amateur radio contacts between students around the globe and crew members with ham radio licenses on the International Space Station (ISS) and develops and operates the amateur radio equipment on ISS.
As part of its ARISS 2.0 initiative, the ARISS International team is expanding its educational and life-long learning opportunities for youth and ham radio operators around the world. ARISS Slow Scan Television (SSTV), which is the transmission of images from ISS using amateur radio, is a very popular ARISS mode of operation. To expand ARISS SSTV capabilities, the ARISS Europe and ARISS USA teams plan to perform special SSTV Experiments using a new SSTV digital coding scheme. For the signal reception, the software “KG-STV” is required, as available on internet.
This is a unique and official ARISS experiment. ARISS kindly request keeping the voice repeater uplink free from other voice transmissions during the experiment time period. Also note that ARISS is temporarily employing the voice repeater to expedite these experiments and make a more permanent, more expansive SSTV capability fully operational on other downlink frequencies.
The first experiment in the series will utilize ARISS approved ground stations in Europe that will transmit these digital SSTV signals. These will be available for all in the ISS footprint when SSTV transmissions occur. The first SSTV experiment is planned for 20 February 2022 between 05:10 UTC and 12:00 UTC for five ISS passes over Europe. Please be aware that this event depends on ARISS IORS radio availabilities and ISS crew support, so last-minute changes may occur.
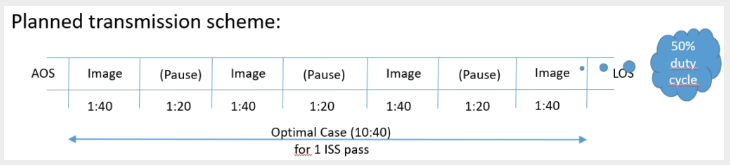
To promote quick experimental SSTV investigations (to learn and improve) the ARISS team will employ the ISS Kenwood radio in its cross-band repeater mode. The crossband repeater operates on a downlink of 437.800MHz. Each transmission sequence will consist of 1:40 minute transmission, followed by 1:20 minute pause and will be repeated several times within an ISS pass over Europe.
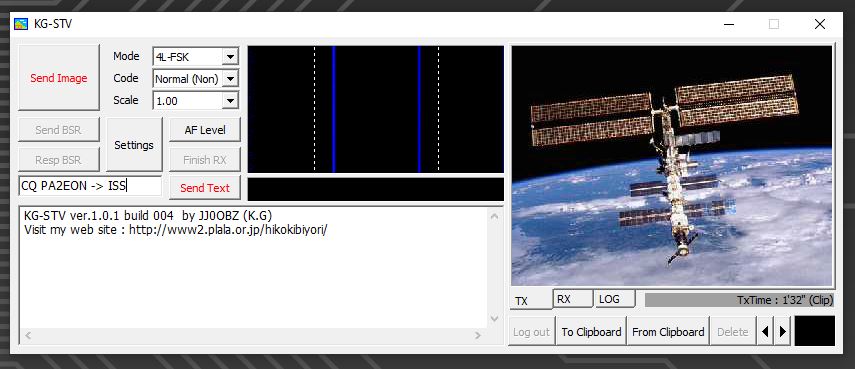
The used modulation is MSK without error correction. For the decoding of the 320x240px image, the software KG-STV is required. The KG-STV software can be downloaded from the following link: http://amsat-nl.org/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/kgstv_ISS.zip.
The ZIP file contains the KG-STV program, an installation and setup manual, some images and MP3 audio samples for your first tests as well as links for additional technical information about the KG-STV use.
Based on what has been read in the manual so far it looks as if the current KG-STV installation is as simple as extracting the ZIP file and running the .EXE file therein, it does not install in the traditional Windows sense. At present there is no Linux or OSX version of the software and the mode is not available in mainstream SSTV programs such as QSSTV or MMSSTV.
2.1 Installation:
Download the ZIP file at sites mentioned in the email you received or ISS publications. Extract the compressed file in the folder you want to.
Go to the folder or make an shortcut to your desktop and start the ‘kgstv.exe’ file. The result will be the next screen:
The members of the ham radio community youth and the public are invited to receive and decode these special SSTV signals.
Experiment reports are welcome and should be uploaded to sstvtest@amsat-on.be.
More information will be available on the AMSAT-NL.org web page: https://amsat-nl.org/?page_id=568.
ARISS indicate that 5 passes are being used for testing:
- 20/02/2022 between 05:12 and 05:24 UTC
- 20/02/2022 between 06:48 and 06:59 UTC
- 20/02/2022 between 08:25 and 08:36 UTC
- 20/02/2022 between 10:01 and 10:14 UTC
- 20/02/2022 between 11:38 and 11:51 UTC
However, for the clubhouse the heavens-above website indicates that only 4 passes rise above 10°, so giving the 05:12 – 05:24 pass a miss might be wise especially given the early hour on a Sunday morning!
Table of ISS Passes
Address: Novers Park Community Association, Rear of 124 Novers Park Road, Bristol, BS4 1RN
- Latitude (degrees N-S where North is +ve): 51.425400°
- Longitude (degrees E-W where East is +ve): -2.593882°
- IARU (Maidenhead) Locator: IO81qk
- Elevation (metres above Ordnance Datum AOD): 64m
- What.Three.Words: ///Weeks.Exams.Flight
If you are reading this News post through Groups.io then, due to formatting limitations imposed by Groups.io, the colour banding may not show up in your post. For a full colour correctly formatted version please head over to the SBARC Website News Page and follow the “Read More” link under the headline and description.
Notes:
In the table below:
- Table Entries with a cyan background indicate passes where: 0° < Maximum Elevation ≤ 30°
- Table Entries with a yellow background indicate passes where: 30° < Maximum Elevation ≤ 45°
- Table Entries with a green background indicate passes where: 45° < Maximum Elevation ≤ 90°
- Times are UK clock time, that is GMT/UTC during the winter and BST/UTC+1:00 during the summer
- Elevation shows the degrees above the horizon. Zero degrees is the horizon and ninety degrees is directly overhead
- Azimuth represents the direction to the ISS using a traditional 16 cardinal point compass rose
| Pass No. |
Date | Acquisition of Signal “AoS” | Maximum Elevation | Loss of Signal “LoS” | Pass Duration (Min:Sec) |
Comments | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | Elevation | Azimuth or Bearing |
Time | Elevation | Azimuth or Bearing |
Time | Elevation | Azimuth or Bearing |
||||
| 1 | 20/02/22 | 06:51:40 | 10° | SW | 06:54:48 | 37° | SSE | 06:57:56 | 10° | E | 06:16 | Daylight |
| 2 | 20/02/22 | 08:28:02 | 10° | W | 08:31:24 | 90° | SSE | 08:34:46 | 10° | E | 06:44 | Daylight |
| 3 | 20/02/22 | 10:04:49 | 10° | W | 10:08:11 | 81° | SSW | 10:11:32 | 10° | ESE | 06:43 | Daylight |
| 4 | 20/02/22 | 11:41:46 | 10° | W | 11:44:41 | 28° | SSW | 11:47:35 | 10° | SSE | 05:49 | Daylight |
If you want to run your own location specific pass predictions try using:
- The AMSAT On line satellite pass predictions
- The Heavens Above website
The AMSAT site will require either:
- Method 1
- Your 6 character IARU (Maidenhead) locator square (e.g. IO81qk); and
- Your elevation in metres (e.g. 64).
- Method 2
- The absolute (without +ve or -ve sign) value of your Latitude in decimal degrees and selecting North where the original value is positive (greater than 0) or selecting South where the original value is negative (less than 0) (e.g. 51.4254 North);
- The absolute (without +ve or -ve sign) value of your Longitude in decimal degrees and selecting East where the original value is positive (greater than 0) or selecting West where the original value is negative (less than 0) (e.g. 2.593882 West);
- Your elevation in metres (e.g. 64).
The Heavens Above site is more flexible and will accept any of:
- Method 1
- Your address including postcode (e.g. Novers Park Community Association, Rear of 124 Novers Park Road, Bristol, BS4 1RN); and
- Your elevation in metres (e.g. 64).
- Method 2
- Your What.Three.Words location descriptor (e.g. ///weeks.exams.flight); and
- Your elevation in metres (e.g. 64).
- Method 3
- Your Latitude in decimal degrees where +ve is north of the equator and -ve is south of the equator (e.g. 51.4254);
- Your Longitude in decimal degrees where +ve is east of the Greenwich Meridian and -ve is west of the Greenwich Meridian (e.g. -2.593882); and
- Your elevation in metres (e.g. 64).
When using Heavens Above don’t forget to check that you have the correct timezone (e.g. (GMT +0:00) United Kingdom/Ireland)
Heavens Above understands British Summer Time and corrects accordingly


